Inspección de la carcasa de aceite en la fábrica
1.1 Frecuencia de inspección
Tabla 1.1 Supervisión de calidad y plan de muestreo
|
Batch Range N |
Sample Size n |
Number of Acceptable Judgments Ac |
Number of Unqualified Judgments Re
|
|
9 ~ 15 |
3 |
0 |
1 |
|
16 ~ 25 |
5 |
0 |
1 |
|
26 ~ 50 |
8 |
0 |
1 |
|
51 ~ 90 |
13 |
1 |
2 |
|
91 ~ 150 |
20 |
2 |
3 |
|
151 ~ 280 |
32 |
3 |
4 |
|
281 ~ 500 |
50 |
5 |
6 |
|
501 ~ 1200 |
80 |
7 |
8 |
|
1201 ~ 3200 |
125 |
10 |
11 |
|
3201 ~ 10000 |
200 |
14 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|

2.Flujo de proceso de la máquina de espesamiento
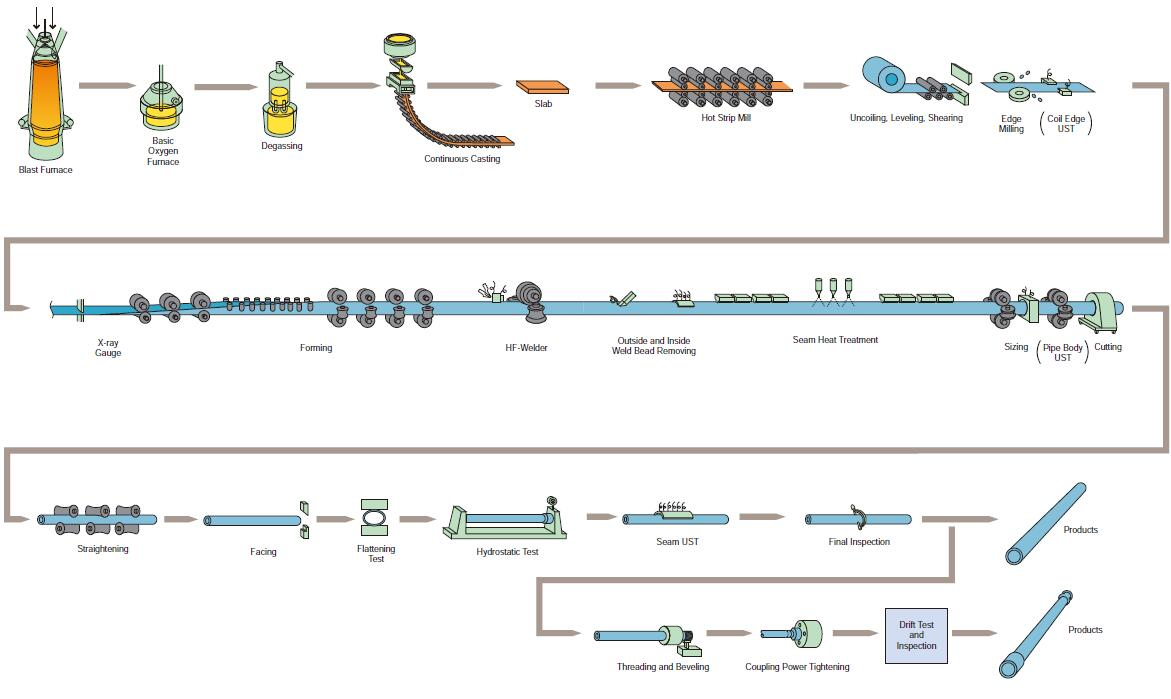
⑴ When thickening pipes of various specifications, it is necessary to select molds of corresponding sizes, check whether the specifications and integrity of the molds meet the production requirements, and install the molds correctly according to the operating procedures. The following table is the mold size required for thickening pipe materials of various specifications:
Table 2.1 60.3*4.83 (type: seamless/ERW; tempered/non-tempered)
|
Specification |
pass |
punch forming area size(mm ) |
punch forging surface siz(mm ) |
punch top to forging surface size(mm ) |
Thickening mold length(mm ) |
moon bend size(mm) |
Clamping die size(mm ) |
Dimensions of the thickening end of the thickening mold(mm) |
|
60.3×4.83 |
first |
51.0 |
63.0 |
≤300 |
500 |
50 |
650 |
64.2 |
|
secondary |
51.0 |
66.5 |
250 |
500 |
50 |
650 |
67 |
|
Table 2.2 73.02*5.51 (type: seamless/ERW; tempered/non-tempered)
|
Specification |
pass |
punch forming area size(mm ) |
punch forging surface siz(mm ) |
punch top to forging surface size(mm ) |
Thickening mold length(mm ) |
moon bend size(mm) |
Clamping die size(mm ) |
Dimensions of the thickening end of the thickening mold(mm) |
|
73.02×5.51 |
first |
63.2 |
75.5 |
≤300 |
500 |
50 |
650 |
76.5 |
|
secondary |
63.2 |
79.5 |
250 |
500 |
50 |
650 |
80.0 |
|
Table 2.3 88.9*6.45 (type: seamless/ERW; tempered/non-tempered)
|
Specification |
pass |
punch forming area size(mm ) |
punch forging surface siz(mm ) |
punch top to forging surface size(mm ) |
Thickening mold length(mm ) |
moon bend size(mm) |
Clamping die size(mm ) |
Dimensions of the thickening end of the thickening mold(mm) |
|
88.9×6.45 |
first |
77 |
92 |
≤300 |
500 |
50 |
650 |
92.7 |
|
secondary |
77 |
96.5 |
250 |
500 |
50 |
650 |
96.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2.4 114.3*6.88 (type: seamless/ERW; tempered/non-tempered)
|
Specification |
pass |
punch forming area size(mm ) |
punch forging surface siz(mm ) |
punch top to forging surface size(mm ) |
Thickening mold length(mm ) |
moon bend size(mm) |
Clamping die size(mm ) |
Dimensions of the thickening end of the thickening mold(mm) |
|
114.3×6.88 |
first |
101.5 |
107.5 |
≤300 |
500 |
50 |
650 |
118.5 |
|
secondary |
101.5 |
121.1 |
250 |
500 |
50 |
650 |
122.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
⑵ At the beginning of production, it is very important to control the spraying time of cooling water, because the production of qualified pipe molds and punches requires a certain temperature, and the length of water spraying time directly affects the temperature of the molds and punches, thus affect the quality of the pipe. Therefore, when producing the first few pipes, the water spray time should be controlled between 7s and 8s to keep the punch and die at a certain temperature, and then the water spray time will be extended as the temperature of the die and punch rises. The control range is generally within Between 10s and 12s. The air injection time is mainly determined by the air flow rate. It is enough to dry the cooling water in the mold of the lower mold. Generally, it is controlled between 1s and 3s;
related suggestion
• Chemical composition of various steel grades of api 5ct oil casing
• Product requirements for J55 and K55 steel grade oil casing in API 5CT
• specifications of API 5CT Grade N80 oil casing
Guess what you want to see
• Grades and Specifications for API 5L Pipe
• Oil Casing Specification Table