Longitudinal welded pipes are made of steel plates or strips that are bent and then welded. According to the weld form, it is divided into straight seam welded pipe and spiral welded pipe. According to the purpose, it is divided into general welded pipe, galvanized welded pipe, oxygen blown welded pipe, wire casing, metric welded pipe, idler pipe, deep well pump pipe, automobile pipe, transformer pipe, electric welded thin-walled pipe, electric welded special-shaped pipe and spiral welded pipe.
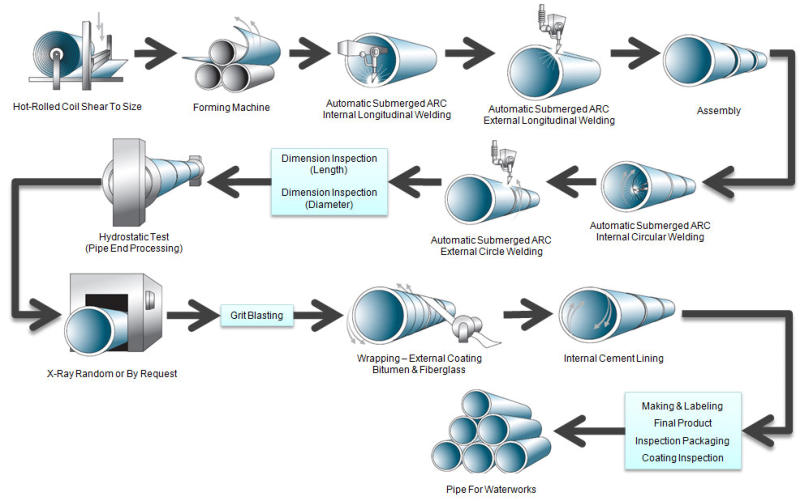
Ⅰ Description of the main production process of large diameter longitudinal welded pipe:
1. Plate inspection: After the steel plate used to manufacture large-diameter submerged arc welded straight seam steel pipes enters the production line, the entire plate is firstly inspected by ultrasonic;
2. Edge milling: use the edge milling machine to perform double-sided milling on both edges of the steel plate to achieve the required plate width, plate edge parallelism and groove shape;
3. Pre-bending: Use a pre-bending machine to pre-bend the edge of the plate so that the edge of the plate has a curvature that meets the requirements;
4. Forming: On the JCO forming machine, first half of the pre-bent steel plate is stamped into a "J" shape by multiple steps, and then the other half of the steel plate is also bent into a "C" shape, and finally the opening is formed. "O" shape
5. Pre-welding: Make the formed straight seam welded steel pipe seam and use gas shielded welding (MAG) for continuous welding;
6. Internal welding: use tandem multi-wire submerged arc welding (up to four wires) to weld on the inside of the straight seam steel pipe;
7. External welding: use tandem multi-wire submerged arc welding to weld on the outside of the straight seam submerged arc welded steel pipe;
8. Ultrasonic inspection Ⅰ: 100% inspection of the inner and outer welds of the straight seam welded steel pipe and the base metal on both sides of the weld;
9. X-ray inspection Ⅰ: 100% X-ray industrial TV inspection for internal and external welds, using image processing system to ensure the sensitivity of flaw detection;
10. Diameter expansion: expand the full length of the submerged arc welded straight seam steel pipe to improve the dimensional accuracy of the steel pipe and improve the distribution of internal stress of the steel pipe;
11. Hydrostatic test: On the hydrostatic testing machine, inspect the expanded steel pipes one by one to ensure that the steel pipes meet the test pressure required by the standard. The machine has automatic recording and storage functions;
12. Chamfering: process the pipe end of the qualified steel pipe to meet the required bevel size of the pipe end;
13. Ultrasonic inspection Ⅱ: Conduct ultrasonic inspection one by one again to check the possible defects of straight seam welded steel pipes after diameter expansion and hydraulic pressure;
14. X-ray inspection II: Carry out X-ray industrial TV inspection and filming of pipe end welds on steel pipes after diameter expansion and hydrostatic test;
15. Tube end magnetic particle inspection: This inspection is carried out to find tube end defects;
16. Anti-corrosion and coating: The qualified steel pipes are anti-corrosion and coating according to user requirements.
Ⅱ Analysis and description of dry welding technology for large-diameter thick-walled welded pipes:
U-shaped grooves or composite grooves are often used for automatic welding of large-diameter and thick-walled (greater than 21mm) pipelines. Due to the time-consuming and labor-intensive processing of U-shaped grooves and composite grooves, the welding efficiency of pipelines is restricted. V-groove processing is simple, time-saving and labor-saving, but when large-diameter and thick-walled pipeline V-groove automatic welding, if the welding process parameters are not selected properly, welding defects will occur.
The welding method adopts STT root welding + CRC-P260 automatic welding machine for heat welding, filling and covering. Welding equipment: Lincoln STT welding machine, Lincoln DC-400, CRC-P260 automatic welding machine. Shielding gas: STT root welding shielding gas 100% CO2, fully automatic welding shielding gas 80% Ar+20% CO2.
Composite groove or U-shaped groove is commonly used in automatic welding, and V-shaped groove can also be used in pipelines with small wall thickness. Their common feature is that the gap on the groove is small. The wall thickness of the second line of the West-East Gas Pipeline is 21.0mm, and the upper opening width of the V-shaped groove is about 22mm, which is close to the swing limit of the CRC-P260 welding torch. Such a groove pattern is a great challenge for automatic welding. The welding process parameters of the automatic welding test were determined according to past experience.
The automatic welding test was carried out with the above parameters. During the test welding, it was found that automatic welds were prone to defects, such as unfused interlayers, unfused side walls, dense pores, and excess height of the overhead welding position.
In order to ensure a good cover forming effect, the cover welding should be done with a smaller
At the same time of welding speed, reduce the swing frequency of the welding torch as much as possible, so that the welding seam on the cover surface is thin and wide, thereby reducing the existence time of the molten pool and achieving the purpose of reducing the residual height of the overhead welding position. According to the test welding results and analysis, the process parameters of STT root welding + CRC automatic welding filling and covering of the connecting line of the second West-East Gas Pipeline were finally determined. Welded according to the welding parameters in Table 3, the weld seam has no defects such as pores, cracks, and lack of fusion after inspection, and the surface shape of the weld seam is good.
The mechanical properties of the welds have been tested by the Welding Technology Center of the China Petroleum and Natural Gas Pipeline Science Research Institute, and all indicators meet the construction requirements of the second line of the West-East Gas Pipeline. The successful application of STT root welding + CRC-P260 automatic welding on large-diameter, thick-walled (V-shaped groove) pipelines fully reflects the characteristics of high-quality, high-efficiency, and low-labor intensity of automatic welding technology.
Ⅲ、Technical requirements and quality inspection of straight seam welded pipes:
According to GB3092 "Welded Steel Pipes for Low-Pressure Fluid Transmission", the nominal diameter of the welded pipe is 6~150mm, the nominal wall thickness is 2.0~6.0mm, and the length of the welded pipe is usually 4~10 meters. factory. The surface quality of the steel pipe should be smooth, and defects such as folding, cracks, delamination, and lap welding are not allowed. The surface of the steel pipe is allowed to have minor defects such as scratches, scratches, weld misalignment, burns and scars that do not exceed the negative deviation of the wall thickness. The thickening of the wall thickness at the weld and the existence of inner seam welding reinforcement are allowed. Welded steel pipes should be subjected to mechanical performance test, flattening test and flaring test, and must meet the requirements of the standard.
The steel pipe should be able to withstand a certain internal pressure, and if necessary, carry out a 2.5Mpa pressure test to keep it leak-free for one minute. The method of eddy current flaw detection is allowed to replace the hydrostatic test. The eddy current flaw detection is carried out according to the standard of GB7735 "Steel tube eddy current flaw detection inspection method". The eddy current flaw detection method is to fix the probe on the frame, keep a distance of 3~5mm between the flaw detection and the weld seam, and conduct a comprehensive scan of the weld seam by the rapid movement of the steel pipe. The flaw detection signal is automatically processed and sorted by the eddy current flaw detector. To achieve the purpose of flaw detection. The welded pipe after the flaw detection is cut off according to the specified length with a flying saw, and it is rolled off the assembly line through the turning frame. Both ends of the steel pipe should be chamfered with flat ends, printed with marks, and the finished pipes are packed in hexagonal bundles before leaving the factory.